
User Story
A user story is a concise, written description of a feature or functionality from an end user's perspective. It serves as a...
Scrum is an agile project management framework that was originally developed for software development projects in the 1990s. It was created by Jeff Sutherland and Ken Schwaber, who based it on their experiences in the software development industry.
Scrum was developed in response to the traditional, Waterfall project management approach, which had several drawbacks. Waterfall projects often suffered from a lack of flexibility, poor communication, and slow progress. The Scrum framework was designed to address these issues by emphasizing collaboration, flexibility, and iterative development.
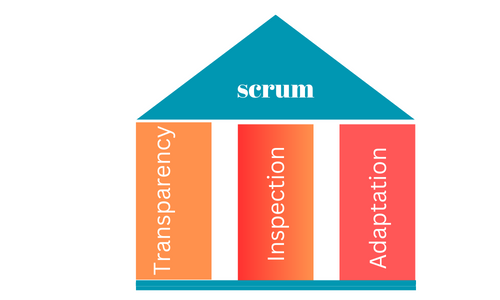
Scrum aims to deliver high-quality software products by emphasizing collaboration, flexibility, and iterative development. The three pillars of Scrum are transparency, inspection, and adaptation.
Transparency is the first pillar of Scrum, and it refers to the concept of openness and visibility in the project’s processes and progress. In a Scrum project, everyone involved should have access to the same information about the project, including the status of the work, progress, issues, and risks. Transparency is achieved through various practices, such as daily Scrum meetings, Sprint Reviews, and Sprint Retrospectives.
Transparency ensures that everyone involved in the project has the same understanding of the project goals, progress, and challenges. It helps to create trust among team members, and stakeholders can make informed decisions based on accurate and timely information.
The second pillar of Scrum is inspection, which involves regularly reviewing the project’s progress to identify any deviations from the plan. In a Scrum project, inspection occurs at multiple levels, including daily Scrum meetings, Sprint Reviews, and Sprint Retrospectives.
The inspection helps to detect problems early, so corrective action can be taken before they escalate. It also helps the team to continuously improve by identifying areas for improvement and implementing changes in the next Sprint.

The third pillar of Scrum is adaptation, which involves making changes to the project based on the results of the inspection. In a Scrum project, adaptation occurs at the end of each Sprint during the Sprint Retrospective. During this meeting, the team discusses the results of the Sprint Review and identifies areas for improvement.
Adaptation helps the team to continuously improve and optimize the project’s processes. It allows the team to respond quickly to changing requirements or market conditions and ensures that the project stays on track to achieve its goals.
Implementing Scrum’s three pillars can bring significant benefits to teams and organizations, but it’s not without its challenges. Here are some common challenges that teams may face when implementing Scrum’s three pillars:
You may also like:
A user story is a concise, written description of a feature or functionality from an end user's perspective. It serves as a...
When implementing Scrum, it is essential to establish clear and specific goals that provide a clear direction and purpose for the project. Clear goals help the Scrum team understand what they need to achieve and why it is important. Effective communication of goals is crucial to align the entire ….
A user story is a concise, written description of a feature or functionality from an end user's perspective. It serves as a...
When implementing Scrum, it is essential to establish clear and specific goals that provide a clear direction and purpose for the project. Clear goals help the Scrum team understand what they need to achieve and why it is important. Effective communication of goals is crucial to align the entire ….
Scrum Artifacts are essential tools in the Scrum framework that provide transparency and help ensure that everyone on the team has a shared understanding of what is being worked on, what needs to be done, and what progress has been made, what has been accomplished, and what still needs to be completed. It can be used for : Prioritize work based on the product vision
0 Comments